Biology Article Enzymes
The reaction converted hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen and oxygen production was used as a measure of enzyme activity. Researchers find that SARS-CoV-2 variants can evade primer-probe sets and recommend that diagnostic assays include multiple targets for reliability.
 Protein The Mechanism Of Enzymatic Action Britannica
Protein The Mechanism Of Enzymatic Action Britannica
Chemical reactions involved in the digestion of foods the biosynthesis of macromolecules the controlled release and utilization of chemical energy and other processes characteristic of life are all catalyzed by enzymes Fig.

Biology article enzymes. Therefore they are called biocatalysts. They are essential for respiration digesting food muscle and. Although RNAs are capable of catalyzing some reactions most biological reactions are catalyzed by proteins.
The Central Role of Enzymes as Biological Catalysts A fundamental task of proteinsis to act as enzymescatalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. The enzyme ketosteroid isomerase KSI rearranges the bonds within its substrate a multi-ring steroid molecule by shifting a hydrogen ion from one carbon to another. In fact there are thousands of different enzymes.
Enzymes are commonly proteinaceous substances which are capable of catalysing chemical reactions of biological origin without themselves undergoing any change. Part of the RNA strand is a substrate for the ribozyme part of the strand. In these reactions the molecules at.
Salivary amylase keeps the pH in the mouth basic. When one substance needs to be transformed into another nature uses enzymes to speed up the process. Coronavirus Mutations Could Muddle COVID-19 PCR Tests.
The inhibitors that do this can do so either reversibly or irreversibly. Quantum Explanations for Biological Phenomena Catherine Offord Jun 1 2019. E studied the effect of temperature enzyme concentration and pH on enzyme activity.
Enzymes are synthesised by living cells. Enzymes are special types of proteins that speed up chemical reactions such as the digestion of food in your stomach. Enzymes are biocatalysts working as highly efficient machines at the molecular level.
Enzyme Enzymes are proteins that catalyze ie. Enzymes cell molecular biology. The enzyme we studied was hydrogen peroxidase from a cow.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity by John Eed Biology 1151 Abstract. Enzymes are biochemical catalysts. In the past enzymes have been viewed as static entities and their function has been explained on the basis of direct structural interactions between the enzyme and the substrate.
One step in this process is the formation of two weak temporary bonds called hydrogen bonds between KSI and an oxygen atom on the substrate. Enzymes cell. Microbes utilize enzymes to perform a variety of functions.
Metabolic processes and other chemical reactions in the cell are carried out by a set of enzymes that are necessary to sustain life. From the remarkable speed of enzyme-catalyzed reactions to the workings of the human brain numerous biological puzzles are now being explored for evidence of quantum effects. The exceptions are a class of RNA molecules known as ribozymes of which most act upon themselves ie.
Salivary amylase will digest starch in your food to maltose which will later get digested to glucose in the Duodenum. They bind to molecules and alter them in specific ways. Enzymes can be slowed down or even prevented from catalyzing reactions in many ways including preventing the substrate from entering the active site or preventing the enzyme from altering conformation to catalyze the reaction.
Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts. Axolotl Academica Publishing Biology at Axolotl Academica Publishing Biological catalysts are called enzymes and the overwhelming majority of enzymes are proteins. Saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase ptyalin.
Enzymes help speed up chemical reactions in the human body. Enzymes can be defined as biological polymers that catalyze biochemical reactions Majority of enzymes are proteins with catalytic capabilities crucial to perform different processes. Lee May 17 2021.
In our stomachs for example enzymes break down food into tiny particles to be converted into energy. Enzymes are biological catalysts also known as biocatalysts that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms and which can be extracted from cells and then used to catalyse a wide range of commercially important processes. A catalytic protein produced by living cells.
 Khan Academy Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Biology Lessons
Khan Academy Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Biology Lessons
 Biology Toolbox Enzyme Substrate Interactions And Inhibition
Biology Toolbox Enzyme Substrate Interactions And Inhibition
 Biology Toolbox Enzyme Substrate Interactions And Inhibition
Biology Toolbox Enzyme Substrate Interactions And Inhibition
 Multi Clean Bio Enzymatic Cleaners How Do They Work Multi Clean
Multi Clean Bio Enzymatic Cleaners How Do They Work Multi Clean
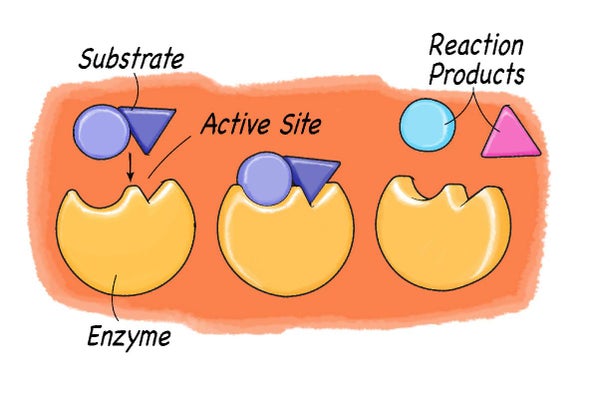 Exploring Enzymes Scientific American
Exploring Enzymes Scientific American
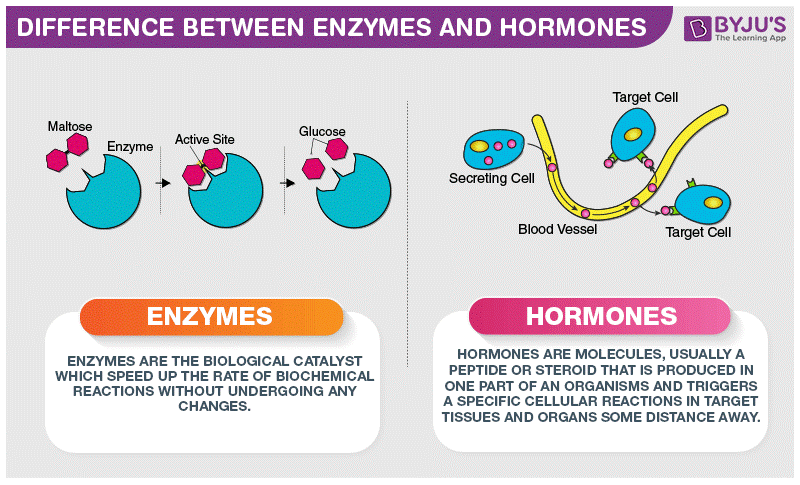 Difference Between Enzymes And Hormones Are Explained In Detail
Difference Between Enzymes And Hormones Are Explained In Detail
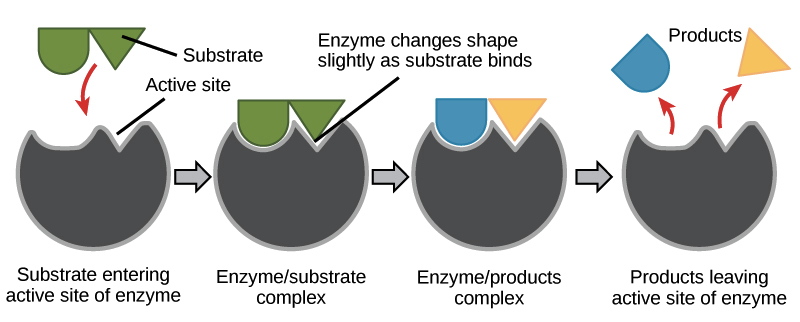 Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy
Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy
 Active Site The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Active Site The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary


 Enzyme Substrate Complex Definition Examples Biology Dictionary
Enzyme Substrate Complex Definition Examples Biology Dictionary
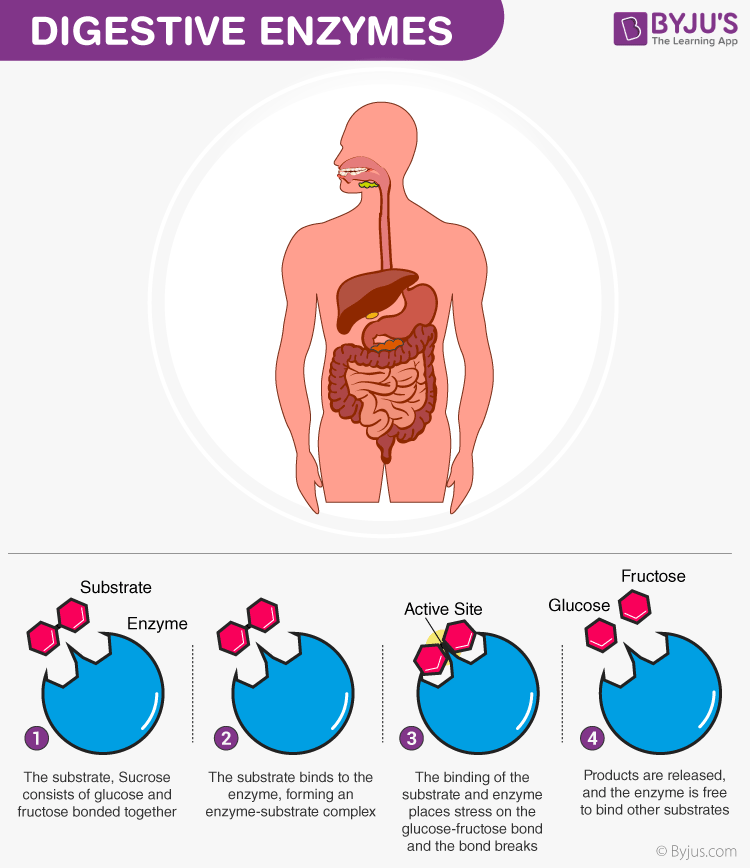 Digestive Enzymes And Its Types Amylase Protease And Lipase
Digestive Enzymes And Its Types Amylase Protease And Lipase

 Enzyme Regulation Article Khan Academy
Enzyme Regulation Article Khan Academy
 Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy
Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy


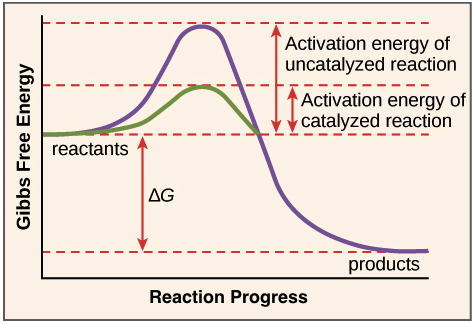 Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy
Enzymes And The Active Site Article Khan Academy
 46 Energy And Enzymes Biology Science Khan Academy Energy Activities Enzymes Biology Competitive Inhibition
46 Energy And Enzymes Biology Science Khan Academy Energy Activities Enzymes Biology Competitive Inhibition
Komentar
Posting Komentar